Hello Everyone, Today we will discuss what is domain and learn about it many computers on the Internet have an address that is unique in nature. It is a string of numbers and is called an IP address. In order to communicate with each other, computers identify the other computer through their IP address. It implements a distributed database that converts IP addresses into a unique alphanumeric address called a domain name.

Basically, a domain name is a sequence of letters and/or numbers separated by one or more periods (“.”). It is like a pointer to a unique IP address on a computer network. As an analogy, one can consider the domain name as the address and the DNS as the address book of the Internet.
Contents
1. What is Domain?

A domain name is a string that identifies the scope of administrative autonomy, authority, or control within the Internet. Domain names are used in various networking contexts and for application-specific naming and addressing purposes. In normal, a domain name identifies a network domain or an Internet Protocol (IP) resource, such as a personal computer used to access the Internet, or a server computer.
Domain names are often used to identify services that are provided through the Internet. Specific to the Internet, the term domain can refer to how the Internet is structured, and domain can also refer to how an organization’s network resources are organized. In general, a domain is an area of control or an area of knowledge.
2. What is an internet domain?
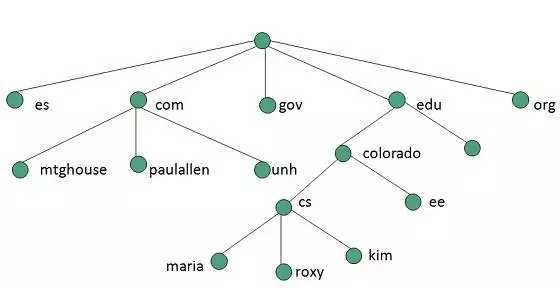
An Internet domain is an administrative structure for organizing, delivering, and accessing services on the Internet. The terms “domain” and “domain name” are often used interchangeably (in the context of the Internet) because the domain structure is associated with the name of the domain.
Internet domains are set up to translate host names into their respective IP addresses according to the Domain Name Service (DNS), an application layer protocol and service used on the network. DNS is an essential component of the Internet. It is implemented as a decentralized, hierarchical system that is globally distributed across a cluster of DNS servers. The service acts as a giant directory for resolving domain names to IP addresses and IP addresses to domain names, regardless of where the domains are located.
3. What are the types of domains
DNS organizes all domain names into a hierarchical structure. At the top of this hierarchy are the various top-level domains, followed by the second and third level domains and sub-domains. All these types of domain names are listed as follows.
Top Level Domains (TLD) – Top-
Level domains are at the highest level in the Internet’s DNS infrastructure. It is also sometimes referred to as expansion. It is further classified into country code TLD and generic TLD, with the country being described as follows.
Country code Top Level Domain (ccDLDs) –
It consists of two-letter domains that include an entry for each country. Example – .in for India, .au for Australia, .us for UN, .jp for Japan etc. It is used by companies and organizations to target local audiences. Only residents of the country are allowed their specified ccTLD, but now some countries have allowed users from outside their country to register their respective ccTLD.

Generic Top Level Domains (gTLDs) -
These are open for registration for all users, regardless of their citizenship, residence or age. Some of gTLDs are .com for commercial sites, .net for network companies, .biz for business, .org for organizations, and .edu for education.
There are many other levels which are below TLD -
Second Level -
It is right below the TLD in the DNS hierarchy. It is also named as label. Example: In .co.in, .co is the second level domain under .in in ccTLD.

Third level -
It is directly below the second level. Example: In yahoo.co.in, .yahoo second level domain under .co is third level domain which is under .in ccTLD.
Sub-domains -
It is part of a higher domain name in the DNS hierarchy. Example: yahoo.com includes a subdomain of the .com domain, and login.yahoo.com includes a subdomain of the .yahoo.com domain.
Also check:
-
Blog Writing vs. Social Media Writing: What's the Difference?
-
5 Best Computer Course in India for Private Job (India में प्राइवेट नौकरी के लिए 05 BEST कंप्यूटर कोर्स)
-
Google jobs in India | Google में चाहिए नौकरी तो कर ये 5 कोर्स - मिलेगा लाखों का पैकेज | Google Jobs
-
Retail Management Career | Retail Jobs | How to get Retail Management Job
-
How to Start Earning as a Graphic Designer?
4. What are the advantages or disadvantages of Domain?
Benefits of domain names – The user does not need to remember the IP address. More reliable and secure.
Disadvantages of Domain Name – Due to many reasons the IP address changes, due to this the IP address of the computer changes but the DNS may have cached the previous IP which will give us wrong information.

5. What is Network Domain?
The term domain is also used in other types of networks to describe the logical organization of the connected physical network resources and users. This type of domain provides a structure to manage network resources and users under the same administrative umbrella. A network domain typically includes servers, desktops, printers and another devices. The network also provides a mechanism to authorize and authenticate users for access
Administrators can control which resources a user can access and the level of access the user has. A network domain usually includes servers, desktops, printers, and other devices. It also provides a mechanism to authorize and authenticate users for network access. Administrators can control which resources a user can access and the level of access the user has.
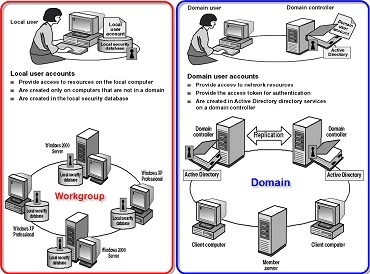
6. What are the difference between Workgroup and Domain
Computers in a domain contain a centralized database.
The computers in the workgroup primarily have their own local database.
A domain is primarily meant to transfer and share only sensitive and important data.
A workgroup is only used to share less secure and personal data because of its low security.
A domain is primarily preferred for large public and business networks.
For small local area networks such as schools, colleges, buildings, etc., primarily a workgroup is preferred.
Data can be retrieved from centralized storage across domains.
Data recovery in a workgroup is not possible due to the local storage of each device.
7. What are the characteristics of Domain?
Here are eight rules that will make choosing the right domain name for your business easier.
Short names are better – Good domains have short names. Technologically, a valid domain name can use up to 63 characters (excluding domain extensions, such as .com, .org or .net). But you want your customers to be able to find you as easily as possible. Short names help reduce the chances of errors in typing, remembering or sharing your name.
Domain names should be easy to remember – in general, you should avoid overly generic names. As with many things related to branding, you will want to differentiate between your company and your offerings. Think about it: Google is such a catchy name. Now consider the name StrongEyeballs.com. It’s over 14 characters long, and it’s currently available as well. Which name is easier to share? You get the idea.
Domain Names Should be Easy to Spell – An effective domain name is easy to spell, pronounce and share. Your goal is to make your site as simple as possible. Avoid any spelling choices that are strange or nonstandard variations of words.
Skip hyphens and numbers – While a domain name can technically include numbers and hyphens, they are not appropriate. Characters other than letters can be confusing (do you type “8” or “eight”?), are challenging to brand and may be considered generic.
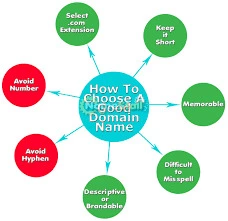
Use the Right Extension – The .com extension is responsible for the overwhelming majority of the world’s top-level domains (TLDs). For most companies, .com is the safest and best option. If possible, buy other top extensions for your domain name (like .net, .org or .guru) and redirect them to your .com site.
Match Your Domain Name to Your Business Brand – Does your domain name make sense or explain the products or services you offer?
Does your name boost your value proposition?
Can people easily remember your name and share it with others?
Is your domain name significantly different from your competitors’ names?
Don’t overplay SEO when choosing a domain name – avoid focusing too much on the keywords for your domain name. At one time, you could improve your search engine rankings by including keywords like “playground-equipment-for-toddlers.com” in your domain.
Check for Trademark and Copyright Issues – Before committing to a site name, make sure it is not subject to trademark or copyright protection. US Go to the Patent and Trademark Office website and search the trademark database, then U.S. Go to the Copyright Office and search the copyright database.
8. Conclusion

We propose that a system similar to the gTLD-MoU be established to allow for international representation, organization and effective conflict resolution. US After considering the green paper, the gTLD-MOU scheme, as well as the current naming system, we feel that the variation of the gTLD-MOU scheme offers the most promise for handling the current naming problems discussed elsewhere in our presentation. The trademark violations that cause many of these problems will be greatly reduced. To facilitate this process, we propose that the Governing Committee, together with the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), create a searchable database of trademarks.
9. FAQ
Specific to the Internet, the term domain can refer to how the Internet is structured, and domain can also refer to how an organization’s network resources are organized. In general, a domain is an area of control or an area of knowledge.
A domain name refers to your website’s address. This is what users type in the search bar of the browser to access your website directly. A domain name is unique and cannot be shared between various sites. For Example: ovhcloud.com.
The local domain is the domain that belongs to your company. For example, if you work for a company called Acme Coffee Shop and you have registered AcmeCoffeeShop.com with Internik, you must specify acmecoffeeshop.com as the local domain.
DNS was created in 1983 and became one of the core Internet standards in 1986 (after the creation of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)). The two documents that mark the commencement are RFC 1034 and RFC 1035. They describe the complete protocol functionality and include the data types it can carry.
Local accounts are stored on computers and only apply to those machines’ security. Domain accounts are stored in Active Directory, and the security settings for the account may be applied when accessing resources and services across the network.
Network devices use IP addresses to communicate with one another. The Internet uses DNS (Domain Name System) to enable people to use words rather than numbers for Internet addresses. You can think of DNS as an Internet address book that maps domain names to IP addresses.
Change the phone’s IP address on
These steps should be applicable on most Android devices. You have to go to Settings > Network and Internet > Wi-Fi. Tap on the network for which you want to change the IP address.


